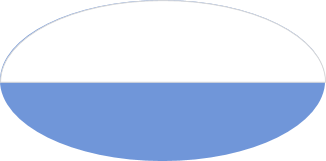
Formation Sign - I ANZAC Corps (World War 1)
Each Corps and Division of the Australian Imperial had a divisional sign. This was a distinct design and not the same as the shoulder flash placed on uniforms. It could be used to mark equipment or supplies intended for a specific unit. The 1 Anzac Corps sign was a 13 point rising sun.
The I ANZAC Corps (First Anzac Corps) was a combined Australian and New Zealand army corps that served during World War I. It was formed in Egypt in February 1916 as part of the reorganisation and expansion of the Australian Imperial Force and the New Zealand Expeditionary Force (NZEF) following the evacuation of Gallipoli in December 1915. Along with the II ANZAC Corps, it replaced the original Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC). The corps initially participated in the defence of the Suez Canal before being transferred to the Western Front in France and Belgium in late March 1916. Later in 1916 the New Zealand Division was removed from I ANZAC's order of battle, swapping with II ANZAC's Australian 4th Division. In November 1917, I ANZAC ceased to exist when the Australian infantry divisions in France were grouped together as the Australian Corps and the New Zealand Division, then part of II ANZAC Corps, was allocated to a British corps.
Details
Details
During World War 1, Australian Corps and Division formation signs were based on a rising sun design although the number of points varied between 9 and 13 This design was based on a trophy of arms which also led to the creation of the rising sun cap badge,
During World War 1, numbered corps utilised Roman numerals. In World War 2, Australian Corps used Arabic numerals.
The marking of military equipment is not a new phenomena. A broad arrow, is a stylised representation of a metal arrowhead, comprising a tang and two barbs meeting at a point. It is a symbol used traditionally in heraldry, and later by the British government to mark government property.
The broad arrow was used in England from the early 14th century, and more widely from the 16th century, to mark objects purchased from the monarch's money, or to indicate government property. It became particularly associated with the Board of Ordnance, and later the War Department and the Ministry of Defence. It was exported to other parts of the British Empire, where it was used in similar official contexts.
The use of markings on Australian military vehicles expanded and became more sophisticated following mass production and the mechanization of armies.
Australian Army Museum of Western Australia
Australian Army Museum of Western Australia
Other items from Australian Army Museum of Western Australia
- Formation Sign - II Anzac Corps (World War 1)
- Formation Sign - ANZAC Mounted Corps (World War 1)
- Formation Sign - Australian Mounted Division (World War 1)
- Formation Signs - Desert Mounted Corps (World War 1)
- Colour Patch - 11 Battalion Australian Imperial Force
- Colour Patch - 16 Battalion Australian Imperial Force
- Colour Patch - 44 Battalion Australian Imperial Force
- Stohwasser Leather Leggings
- Australian Army Issue Spurs
- 1903 Pattern Bandoliers
- World War 1, 1912 Universal Pattern Saddle
- World War 1, 1912 Universal Pattern Saddle - Equipage - Horse Shoe Carrier

Scan this QR code to open this page on your phone ->