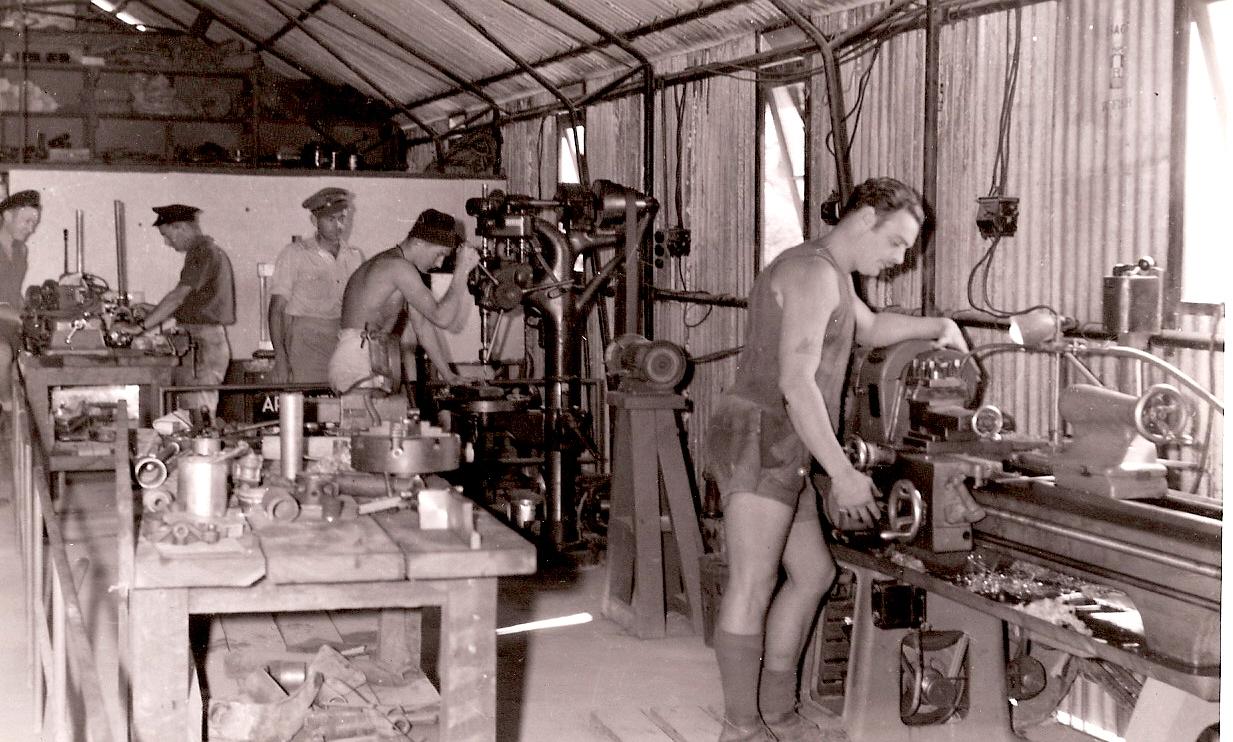
World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Exmouth Gulf, Potshot, 1942
1942View of interior of Potshot workshop
During World War II a little-known landing field was constructed on the western shore of Exmouth Gulf. It was code-named "Potshot" and maintained by No. 76 Operational Base Unit. In the 1950s the landing field was further developed as a military base and named RAAF Learmonth in honour of Wing Commander Charles Learmonth DFC and Bar, who, while leading No. 14 Squadron, was killed in a flying accident off Rottnest Island, Western Australia on 6 January 1944. The Bay of Rest on the southern side of the Exmouth Gulf was used for anchorage for refuelling submarines on the way north from Fremantle. Construction on the base began in the latter part of 1942.
Starting in June 1944, Qantas used Learmonth as an intermediate stop for two converted Consolidated Liberator bombers that flew a segment of the vital England–Australia air route, supplementing modified Consolidated PBY Catalinas flying The Double Sunrise route to Ceylon. The Liberators flew a shorter 4,952 km over-water route from Learmonth to an airfield northeast of Colombo, and could make the journey in 17 hours with 2,500 kg of payload, whereas the Catalinas usually required at least 27 hours and had to carry so much auxiliary fuel that their payload was limited to only 450 kg. The route was named Kangaroo Service and marked the first time that Qantas's now-famous Kangaroo logo was used; passengers received a certificate proclaiming them as members of The Order of the Longest Hop.
Details
Details
Open in Google Maps
Nearest geotagged records:
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Heavy Anti-Aircraft, 1943 (0km away)
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Exmouth Gulf, 140 Heavy Anti Aircraft Battery, 1943 (0km away)
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, Exmouth Gulf, 151 Light Anti Aircraft Battery Camp, 1942 (0km away)
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, 1942 (0km away)
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Exmouth Gulf, Light Anti Aircraft, 1942 (0km away)
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Exmouth Gulf, Anti-Aircraft defences,1943 (0km away)
- World War 2, Australia Western, Australia, Exmouth Gulf, Light Anti-Aircraft Battery, 1943 (0km away)
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Exmouth Gulf, Potshot, 1942 (0.3km away)
Australian Army Museum of Western Australia
Australian Army Museum of Western Australia
More items like this
Other items from Australian Army Museum of Western Australia
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, STOKES-HEWES,1942
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, 1942
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, DARCY DAVIES, 1942
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, Exmouth Gulf, 151 Light Anti Aircraft Battery Camp, 1942
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, 1942
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Exmouth Gulf, Light Anti Aircraft, 1942
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, 1942
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, STOKES-HUGHES, 1942
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Nullabor, 1942
- World War 2, Australia Western Australia, 1942
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, Australian Women's Army Service, 1943
- World War 2, Australia, Western Australia, South West Pacific, Papua New Guinea, Lae, Australian Women's Army Service, 1945